Adobe Digital Foundation Blueprint
The foundation of a scalable website based on AEM and Adobe Commerce (Magento)
Adobe Digital Foundation Blueprint as the foundation of a scalable website in combination with Adobe Commerce
The Adobe Digital Foundation Blueprint is a project blueprint with a set of open source tools, best practices documentation, and automation.
Adobe's goal - and ours as a verified partner - is to provide users with an AEM sites environment with personalization and analytics capabilities in a short period of time. To do this, there are several building blocks that allow IT and marketing departments to grow together across platforms.
Technology as the key to the concept
With the Digital Foundation Blueprint, Adobe offers the right tool for a successful project plan and supports individual phases of a project.
Adobe's content management system (CMS) connects individual components so that they can communicate with each other across platforms and data can be processed uniformly. You have the option of using AEM as a standalone or cloud service. Here, Adobe provides the right tools to create a ready-for-go-live site in a time-efficient manner.
The archetype is a Maven command to set up and configure an AEM project with defined parameters. This serves as a template to have ready-made configurations for your own use case, saving developer resources.
Example of an archetype:
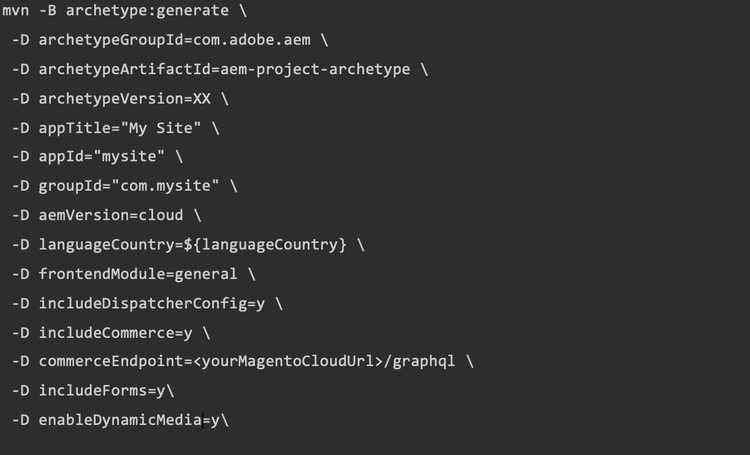
Other features include initial configuration of a cloud-ready instance, preparation for a multi-language site and a WebApp-ready environment with e.g. React or Angular. For improving website speed and security, the archetype can include a dispatcher configuration.
A complete list of the various parameters can be found at the following link: https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/experience-manager-core-components/using/developing/archetype/overview.html
The latest archetype requires Java SE 8 or 9 and additionally Maven version 3.3.9 or newer.
The SDK for the cloud environment can be downloaded from the following link: https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/experience-manager-learn/cloud-service/local-development-environment-set-up/overview.html
Core Components form the core of the project. These components, which are already integrated, make it possible to create initial content on a website in a short amount of time. Initial standard functions and configurations are thus already provided.
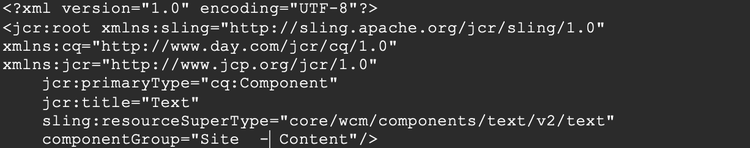
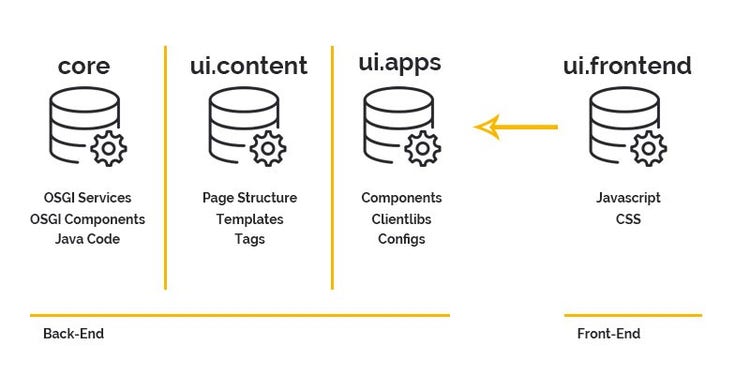
For the front-end workflows, you can choose between two different build variants and use the one that suits your project:
- Webpack (https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/experience-manager-core-components/using/developing/archetype/uifrontend.html?lang=en#webpack-dev-server): The required CSS and JavaScript files are places or customized in the appropriate folder and the Webpack build is started by an npm run command.
- Storybook (https://storybook.js.org/): However, it should be noted here that this is not already integrated into AEM and must be installed manually.
- Basically, you can also use existing templates that already contain a selection of page templates, editable content and dummy images. The already created pages and components save time and after a short time you have a website that you can go live with. As an editor, you only have to adjust the texts and images. With the prefabricated components and templates you can quickly and easily create additional pages.
A good example of this is the WKND tutorial provided by Adobe (https://wknd.site/us/en.html), which you can check out at the following Github link (https://github.com/adobe/aem-guides-wknd/releases/tag/aem-guides-wknd-1.0.0).
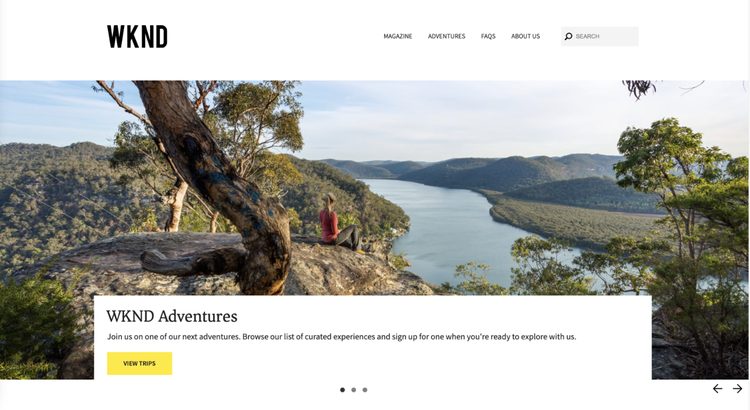
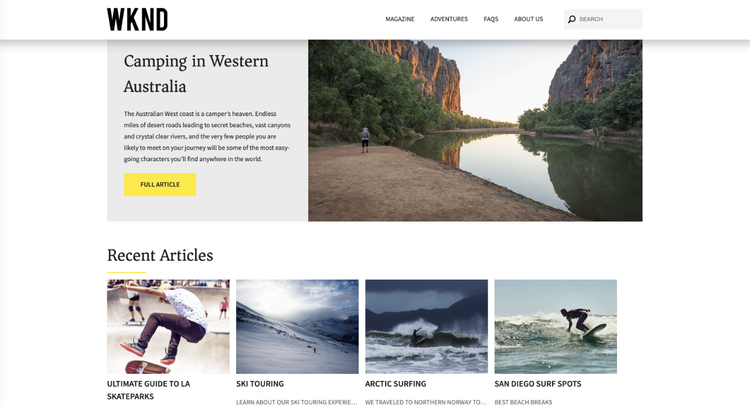
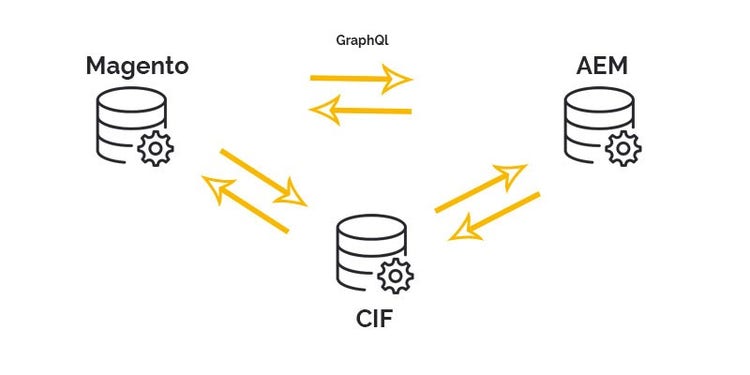
The Commerce Integration Framework (CIF) as an interface to AEM and Adobe Commerce
Adobe Experience Manager and Adobe Commerce (Magento) are seamlessly integrated using the Commerce Integration Framework (CIF). The CIF enables AEM to directly process the data provided by the GraphQL interface and establish communication between AEM and the Commerce instance.
The separation of the Commerce and CMS systems provides different types of integration. It is possible to integrate Adobe Commerce as a standalone, i.e. separate instance, or headless into an already existing environment.
With a headless integration into an AEM instance GraphQL is used as interface. Here, after a request, one receives a JSON response from the products maintained in Magento.
Request:

Response:

The data is displayed and created in the Commerce category of the AEM environment so that it can be easily used when editing a page in the component configuration.
The existing CIF components are built on REACT and can be quickly customized as needed.
In the local development environment, it is therefore important to define a commerceEndpoint before starting AEM. This can be set by the following terminal command in your AEM project structure.


Now you have the possibility to customize the Commerce components.
After making changes, you should run an npm run build command so that the CSS file is regenerated and minimized.
You can find it under the following path:

The foundation is set - now what?
Now that the foundation has been adjusted to the needs of the project and you have a running site, the question is what to do next.
Again, Adobe offers a guide for further processes and recommends that you now take care of optimizing the site. The in-house services Adobe Analytics and Adobe Target can be integrated seamlessly and offer the advantage that all data is in one environment.
Through Adobe Analytics, you can track exactly where visitors come from and how they behave on the site. This allows for detailed analytics to optimize the user experience.
Adobe Target provides the ability to use analytics data to define audiences and deliver personalized offers or advertising. This allows visitors to see relevant information more quickly, which leads to more positive user behavior.
Summarized
The motto "quick time-to-value" fully applies, thanks to Archetype and the associated running AEM environment, the prefabricated components and the templates. Resources can thus be focused on further development. The different ways to link instances provide flexibility for any use case.
Adobe Commerce (Magento), for example, can be operated as a standalone server. The headless integration of the commerce environment can be easily accomplished through the provided GraphQl interface and the CIF components.
Thus, the products with prices, images and descriptions can be maintained in Magento and then used in the likewise independent AEM environment.
